1 工具集#
1.2 字符串工具集 StringUtils#
public class StringUtils extends org.springframework.util.StringUtils
在类的签名上继承于spring的StringUtils,所以该类包含基本的isEmpty()、concatenateStringArrays()等方法。下面介绍再其上新添加的方法:
1.2.1 cropUrl#
裁剪带有请求参数的url。
/**
* 裁剪带有请求参数的url。<br/>
* example:https://passport.baidu.com/passApi/js/wrapper.js?cdnversion=1638804235178&_=1638804234866<br/>
* or<br/>
* https://passport.baidu.com/passApi/{id}/{name}<br/>
* <b>给定规则:</b><br/>
* <i>1.请求链接中如果存在带有"?"并且后面跟有参数,那么把"url"裁剪成http://localhost/api, 其余的参数通过sink或者consumer进行消费</i><br/>
* <i>2.请求链接中入股存在"{id}"的占位符格式,那么保留这个url。"id"这个参数通过sink或者consumer进行消费</i><br/>
* <i>3.请求链接同时存在"?"与"{id}", 那么按照1与2的规则进行裁剪</i>
*
* @param url 请求url
* @return 裁剪完没有带请求的地址
*/
public static String cropUrl(String url, FluxSink<Tuple2<String, List<String>>> sink) {
...
}
使用示例:
/**
* 测试裁剪时发送参数
*/
@Test
void testCuttingEmitterParameter() {
String url = "https://ss0.baidu.com/6ONWsjip0QIZ8tyhnq/it/u=271657503,3457309198&fm=179&app=35&f=PNG?w=96";
AtomicReference<FluxSink<Tuple2<String, List<String>>>> emitter = new AtomicReference<>();
Flux.create(emitter::set)
.subscribe(tuple2 -> {
assertEquals("w", tuple2.getT1());
assertEquals("96", tuple2.getT2().get(0));
});
StringUtils.cropUrl(url, emitter.get());
}
1.2.2 joinUrl#
在url中拼接参数。
/**
* 向url链接中拼接vars的内容<br/>
* example:https://passport.baidu.com/passApi/js/wrapper.js?cdnversion=1638804235178&_=1638804234866<br/>
* or<br/>
* https://passport.baidu.com/passApi/{id}/{name}<br/>
* <b>拼接分为两部分:</b><br/>
* <i>1.占位符替换</i><br/>
* <i>2.参数的拼接</i>
*
* @param templateUrl 模板url链接
* @param vars 参数Map集合
* @return 拼接完成后的url地址
* @throws IllegalArgumentException 参数为空时抛出异常
*/
public static String joinUrl(String templateUrl, Map<String, ?> vars) {
...
}
使用示例:
/**
* 测试拼接多个参数
*/
@Test
void testJoinMultiParameter() {
String url = "https://www.json.cn/index.php";
Map<String, String> vars = new HashMap<>();
vars.put("s", "api");
vars.put("app", "blog");
vars.put("c", "tran");
vars.put("m", "get_user_status");
String joinUrl = StringUtils.joinUrl(url, vars);
assertEquals("https://www.json.cn/index.php?app=blog&s=api&c=tran&m=get_user_status", joinUrl);
}
1.2.3 getBaseUrl#
/**
* 获取url中基础的地址<br/>
* example: https://passport.baidu.com/passApi/js/wrapper.js?cdnversion=1638804235178&_=1638804234866<br/>
* result:passport.baidu.com
*
* @param templateUrl 请求链接
* @return 解析完成的地址
*/
public static Mono<String> getBaseUrl(String templateUrl) {
...
}
1.2.4 getApiUrl#
/**
* 获取url中api的地址
* example: https://passport.baidu.com/passApi/js/wrapper.js<br/>
* result:/passApi/js/wrapper.js
*
* @param templateUrl 请求链接
* @return 解析完成的地址
*/
public static Mono<String> getApiUrl(String templateUrl) {
...
}
1.2.5 getHost#
/**
* 获取url中主机地址<br/>
* example: passport.baidu.com:8080
* result: passport.baidu.com
*
* @param templateUrl 请求链接
* @return 解析完成的地址
*/
public static Mono<String> getHost(String templateUrl) {
...
}
1.2.6 getPort#
/**
* 获取url中主机端口<br/>
* example: passport.baidu.com:8080
* result: 8080
*
* @param templateUrl 请求链接
* @return 解析完成的端口
*/
public static Mono<Integer> getPort(String templateUrl) {
...
}
1.3 ResourceUtils#
用于类路径下资源的加载于解析,基于springResourceUtils
1.4 Requires#
关于方法参数验证的类,如果要验证不通过将抛出一个统一的异常。
1.5 反射 ReflectUtils#
1.6 ObjectUtils#
1.7 NumberUtils#
1.8 JsonUtils#
1.9 IoUtils#
1.10 FileUtils#
1.11 DateUtil#
1.12 CoreBeanUtil#
Spring Bean工具方法
1.13 ConvertUtil#
1.14 CollectionUtils#
1.15 ClassUtils#
1.16 CalendarUtil#
1.17 BigDecimalUtil#
1.18 template#
在实际字符串解析过程,常常会有模板占位符的替换,如mybatis的xml编写,SpEL表达式的编写。基于这种需求在template包下包含以模板表达式的解析。
public interface ExpressionTemplate {
/**
* Express模板文件的后缀
*/
String FILE_SUFFIX = ".template";
/**
* 解析模板,当发生错误时将保持原样
*
* @param template 模板
* @param target 填充于模版的目标对象,要求是一个POJO对象
* @return 解析完成的字符串
* @throws NullPointerException template target为空时抛出
*/
String parseTemplate(String template, Object target);
// 方法省略
...
}
在ExpressionTemplate接口中,定义了模板解析的模板方法,通过传入指定的模板字符串和对应用于解析的对象(可能是POJO、Map、List…)。
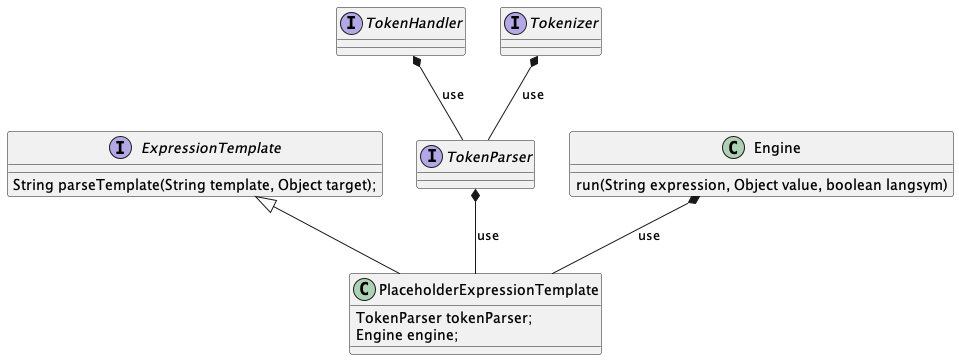
TokenParser:通过把文本逐个翻译成字节后与给定的Tokenizer比较,如果匹配则调用TokenHandler做进一步处理,在PlaceholderExpressionTemplate中:
public class PlaceholderExpressionTemplate implements ExpressionTemplate {
private final TokenParser tokenParser;
private final Engine engine;
private final boolean langsym;
PlaceholderExpressionTemplate(Tokenizer tokenizer) {
this(tokenizer, false);
}
PlaceholderExpressionTemplate(Tokenizer tokenizer, boolean langsym) {
this.tokenParser = new GenericTokenParser(tokenizer);
this.engine = new SymbolEngine(StringPool.DOT);
this.langsym = langsym;
}
@Override
public String parseTemplate(@NonNull String template, @NonNull Object target) {
return tokenParser.parse(template, expression -> {
try {
return engine.run(expression, target, langsym);
} catch (Throwable e) {
return expression;
}
});
}
}
经过回调调用Engine做进一步处理。
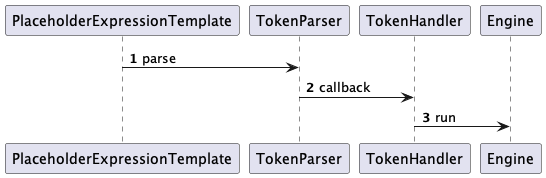
使用示例:
@Override
protected void onInit() throws Throwable {
template = new PlaceholderExpressionTemplate(Tokenizer.HASH_BRACE);
user = new User();
user.setId("1");
System system = new System();
system.setId("2");
user.setSystem(system);
}
@Test
void testPlainText() {
String plain = "#{id} - #{system.id}";
String r = template.parseTemplate(plain, user);
assertEquals("1 - 2", r);
}
1.19 id#
在系统常用需要生成唯一id,在core中有通用工具类:IdGenerator
Long nextId = IdGenerator.defaultGenerator().getNextId();
2 事件总线#
事件总线基于主题(Topic)-发布(Publish)-订阅(Subscribe)模式,其中传播模型通过Topic-Notic-Event进行绑定。包含以下几个组件:
- 发布者(Publisher):发布事件(数据)到事件总线上,使得订阅者(Subscriber)能够接受数据。
- 订阅者(Subscriber):订阅者通过订阅自己感兴趣的事件,当事件到来时触发相应的动作。
- 事件(Event):事件是一个抽象的模型,表明系统中存在的状态、动作的变化。
- 主题(Topic):发布者与订阅者之间的联系,主题路径以’/’的形式(如/t1/t2)构成一颗主题树,支持通配符形式(如/t1/**),当发布者向
/t1/t2发布事件,订阅者/t1/**就能收到该事件。 - Node:订阅者的模型。
- Notic:从Topic连接到Node之间的桥梁组件。
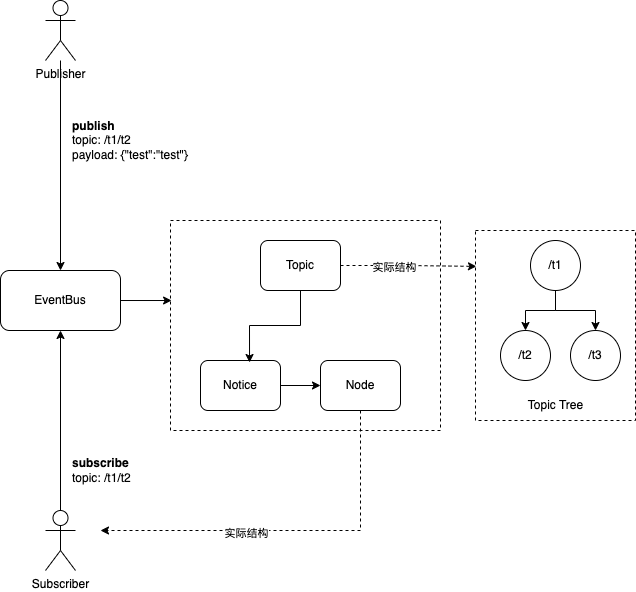
下面为EventBusApi定义:
public interface EventBus<C extends EventContext> {
/**
* 根据主题路径获取指定的主题实例
*
* @param topicKey topicKey
* @return Topic stream or empty stream
*/
default Flux<Topic<C>> findTopic(TopicKey topicKey) {
return findTopic(topicKey.getSubscription());
}
/**
* 根据主题路径获取指定的主题实例
*
* @param path 主题路径
* @return Topic stream or empty stream
*/
default Flux<Topic<C>> findTopic(String path) {
return findTopic(Subscription.of(path));
}
/**
* 根据主题路径获取指定的主题实例
*
* @param subscription 订阅实例
* @return Topic stream or empty stream
*/
Flux<Topic<C>> findTopic(Subscription subscription);
/**
* 批量订阅事件总线
*
* @param subscriptions 订阅集合
* @return 多源的数据流
* @see #subscribe(Subscription)
*/
default Flux<Node<C>> subscribe(List<Subscription> subscriptions) {
return Flux.fromIterable(subscriptions).flatMap(this::subscribe);
}
/**
* 订阅该事件总线,如果没有生成{@link Topic}将会先生成Topic。
* <b>不支持重复订阅,第一次订阅时返回流数据,后面针对同一个订阅都是空流</b>
*
* @param path 主题(可以是通配符/test/*,订阅test下所有主题)
* @return 返回指定Topic下新的Node实例
*/
default Flux<Node<C>> subscribe(String path) {
return subscribe(Subscription.of(path));
}
/**
* 订阅该事件总线,如果没有生成{@link Topic}将会先生成Topic。
* <b>不支持重复订阅,第一次订阅时返回流数据,后面针对同一个订阅都是空流</b>
*
* @param topicEvent 主题事件(可以是通配符/test/*,订阅test下所有主题)
* @return 返回指定Topic下新的Node实例
*/
default Flux<Node<C>> subscribe(TopicEvent topicEvent) {
return subscribe(topicEvent.getTopicKey().getSubscription());
}
/**
* 订阅该事件总线,如果没有生成{@link Topic}将会先生成Topic。
* <b>不支持重复订阅,第一次订阅时返回流数据,后面针对同一个订阅都是空流</b>
*
* @param subscription 订阅消息
* @return 返回指定Topic下新的Node实例
* @see #subscribeOnRepeatable(Subscription)
*/
Flux<Node<C>> subscribe(Subscription subscription);
/**
* 订阅该事件总线,如果没有生成{@link Topic}将会先生成Topic。
* <b>支持重复订阅</b>
*
* @param subscriptions 订阅集合
* @return node stream
*/
default Flux<Node<C>> subscribeOnRepeatable(List<Subscription> subscriptions) {
return Flux.fromIterable(subscriptions).flatMap(this::subscribeOnRepeatable);
}
/**
* 订阅该事件总线,如果没有生成{@link Topic}将会先生成Topic。
* <b>支持重复订阅</b>
*
* @param path 主题路径
* @return node stream
*/
default Flux<Node<C>> subscribeOnRepeatable(String path) {
return subscribeOnRepeatable(Subscription.of(path));
}
/**
* 订阅该事件总线,如果没有生成{@link Topic}将会先生成Topic。
* <b>支持重复订阅</b>
*
* @param topicEvent 主题事件
* @return node stream
*/
default Flux<Node<C>> subscribeOnRepeatable(TopicEvent topicEvent) {
return subscribeOnRepeatable(topicEvent.getTopicKey());
}
/**
* 订阅该事件总线,如果没有生成{@link Topic}将会先生成Topic。
* <b>支持重复订阅</b>
*
* @param topicKey 主题键
* @return node stream
*/
default Flux<Node<C>> subscribeOnRepeatable(TopicKey topicKey) {
return subscribeOnRepeatable(topicKey.getSubscription());
}
/**
* 订阅该事件总线,如果没有生成{@link Topic}将会先生成Topic。
* <b>支持重复订阅</b>
*
* @param subscription 订阅消息
* @return node stream
*/
Flux<Node<C>> subscribeOnRepeatable(Subscription subscription);
/**
* 向消息指定{@link Topic}解除当前{@link Node}。<br/>
* {@link Node#doLift(LongConsumer)}}事件
*
* @param listenerId 监听id
* @param topicKey topicKey
*/
default void unSubscribe(Long listenerId, TopicKey topicKey) {
unSubscribe(listenerId, topicKey.getPath());
}
/**
* 向消息指定{@link Topic}解除当前{@link Node}。<br/>
* {@link Node#doLift(LongConsumer)}}事件
*
* @param listenerId 监听id
* @param topic 消息主题
*/
void unSubscribe(Long listenerId, String topic);
/**
* 从事件总线释放指定的topic
*
* @param topicKey topic唯一标识
*/
default void releaseTopic(TopicKey topicKey) {
releaseTopic(topicKey.getPath());
}
/**
* 从事件总线释放指定的topic
*
* @param topic topic唯一标识
*/
void releaseTopic(String topic);
/**
* 同一个上下文,批量发布数据
*
* @param subscriptions 订阅信息集合
* @param context 时序上下文
* @see #publish(Subscription, C)
*/
default void publish(List<Subscription> subscriptions, C context) {
subscriptions.forEach(subscription -> publish(subscription, context));
}
/**
* 向事件总线发布数据,数据将会在当前路径Topic中所有{@link Node#doEmmit(Consumer)}被接受
*
* @param subscription 订阅信息数据
* @param context 主题上下文
*/
default void publish(Subscription subscription, C context) {
publish(subscription.getPath(), context);
}
/**
* 向事件总线发布数据,数据将会在当前路径Topic中所有{@link Node#doEmmit(Consumer)}被接受
*
* @param topicEvent topicEvent
*/
default void publish(TopicEvent topicEvent) {
topicEvent.getEventContext().getEventTracer().push(topicEvent);
publish(topicEvent.getTopicKey().getPath(), (C) topicEvent.getEventContext());
}
/**
* 向事件总线发布数据,数据将会在当前路径Topic中所有{@link Node#doEmmit(Consumer)}被接受
*
* @param path 订阅主题路径
* @param context 主题上下文
*/
default void publish(String path, C context) {
publishOnFlux(path, context).subscribe();
}
/**
* 向事件总线发布数据,数据将会在当前路径Topic中所有{@link Node#doEmmit(Consumer)}被接受
*
* @param topicEvent topicEvent
*/
default Flux<Topic<C>> publishOnFlux(TopicEvent topicEvent) {
topicEvent.getEventContext().getEventTracer().push(topicEvent);
return publishOnFlux(topicEvent.getTopicKey().getPath(), (C) topicEvent.getEventContext());
}
/**
* 批量向事件总线发布数据,数据将会在当前路径Topic中所有{@link Node#doEmmit(Consumer)}被接受
*
* @param topicEvents topicEvents
* @return Topic - flux
*/
default Flux<Topic<C>> publishOnFluxForMulti(List<TopicEvent> topicEvents) {
return Flux.fromIterable(topicEvents)
.flatMap(this::publishOnFlux)
.distinct();
}
/**
* 向事件总线发布数据,数据将会在当前路径Topic中所有{@link Node#doEmmit(Consumer)}被接受
*
* @param path 订阅主题路径
* @param context 主题上下文
* @return flux
*/
Flux<Topic<C>> publishOnFlux(String path, C context);
/**
* 先进行订阅之后发布数据
*
* @param topicEvent topicEvent
* @return Topic - flux
*/
default Flux<Topic<C>> subThenPub(TopicEvent topicEvent) {
subscribeOnRepeatable(topicEvent).subscribe();
return publishOnFlux(topicEvent);
}
}
2.1 基本使用#
EventBusTest.java#
private final EventBus<EventContext> bus = new DefaultEventBus();
@Test
void testSubscribe() {
// 获取订阅的node
bus.subscribe(Subscription.of("1"))
.map(node -> node.reply(EmitEvent.class, eventContext -> assertEquals("1", eventContext.getTopicPath())))
.as(StepVerifier::create)
.expectNextCount(1)
.verifyComplete();
// 转换为 event context
bus.subscribe(Subscription.of("1"))
.flatMap(Node::onNext)
.doOnNext(System.out::println)
.subscribe();
bus.subscribe(Subscription.of("2"))
.map(node -> node.reply(EmitEvent.class, eventContext -> assertEquals("2", eventContext.getTopicPath())))
.as(StepVerifier::create)
.expectNextCount(1)
.verifyComplete();
bus.publish(Subscription.of("1"), new DefaultEventContext(Collections.emptyMap()));
bus.publish(Subscription.of("2"), new DefaultEventContext(Collections.emptyMap()));
}
@Test
void testWildcard() {
bus.subscribe(Subscription.of("/t1/**"))
.map(node -> node.reply(EmitEvent.class, eventContext -> System.out.println(eventContext.getTopicPath())))
.as(StepVerifier::create)
.expectNextCount(1)
.verifyComplete();
bus.subscribe(Subscription.of("/t2/**"))
.map(node -> node.reply(EmitEvent.class, eventContext -> System.out.println(eventContext.getTopicPath())))
.as(StepVerifier::create)
.expectNextCount(1)
.verifyComplete();
bus.publish(Subscription.of("/t1/t2"), new DefaultEventContext(Collections.emptyMap()));
bus.publish(Subscription.of("/t1/t2/t3"), new DefaultEventContext(Collections.emptyMap()));
bus.publish(Subscription.of("/t2/t1/t3"), new DefaultEventContext(Collections.emptyMap()));
bus.publish(Subscription.of("/t2/t1/t3"), new DefaultEventContext(Collections.emptyMap()));
}
3.元数据转换#
对于一个结构化数据,不论是一个对象还是json数据,都含有其标准的格式。
{
"k1":"v1"
}
public class Demo {
private String id;
...
}
利用这个格式我们就可以对他进行描述,如类的字段名与他的值,json数据的key与他的值…利用这个特性可以通过对描述的数据进行搜集、转换为另一种数据…
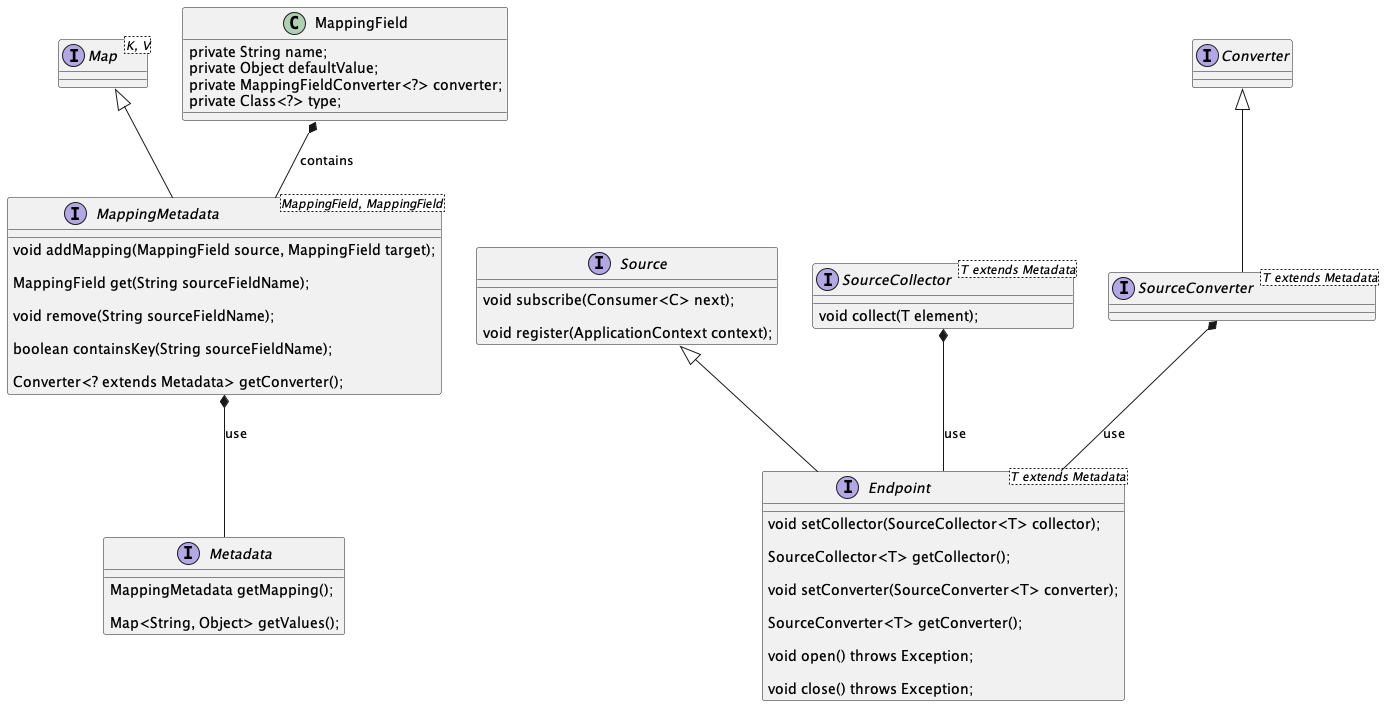
在如上面的简易类图中,我们可以看到它怎么描述元数据,以及其定义和元数据字段的定义。在图的右侧部分,则是它进行数据搜集,转换以及下游处理的过程。通过Endpoint这个桥接器,连接了Source、SourceCollector、SourceConverter三者。
简单示例:
DefaultEndpointTest.java#
@Test
void testCollect() {
DefaultEndpoint<UserMetadata> endpoint = new DefaultEndpoint<>();
TestSourceConverter converter = new TestSourceConverter();
endpoint.setConverter(converter);
TestSourceCollector collector = new TestSourceCollector();
endpoint.setCollector(collector);
// 设置数据源
endpoint.registerSource(new CollectionSource(
Lists.newArrayList(new User("id", "name", ""))));
try {
endpoint.open();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
assertEquals(1, collector.size());
}
4.功能链#
功能链本身不具备任何功能,它通过API来描述责任链模式,有三个角色:
Chain:责任链本身。Node:在链中的节点.ChainContext:执行过程的上下文。
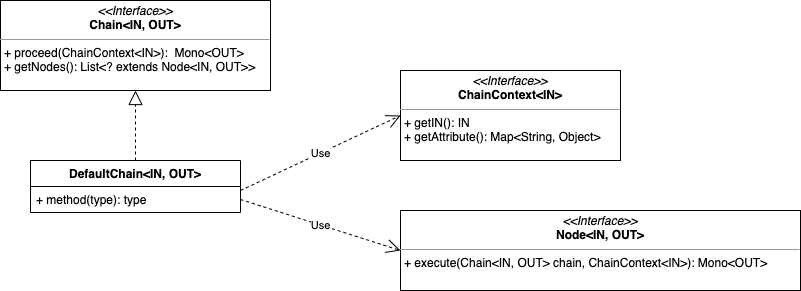
在这个基础上,uno通过使用它完成了Http请求链的封装。
简单使用:
DefaultChainTest.java#
@Test
void testNodeContext() throws Throwable {
TestNode1 node1 = new TestNode1();
TestNode2 node2 = new TestNode2();
DefaultChain<String, String> chain = new DefaultChain<>(Arrays.asList(node2, node1));
TestChainContext context = new TestChainContext();
chain.proceed(context)
.as(StepVerifier::create)
.verifyComplete();
}